As someone who grew up in the last days of the British Empire, I am often asked how it was that so few people controlled so much of the world for so long?
The simple answer is technology underpinned the British Empire, from its tentative beginnings in the 17th century to its global dominance in the 18th and 19th centuries and most of the first half of the 20th century.
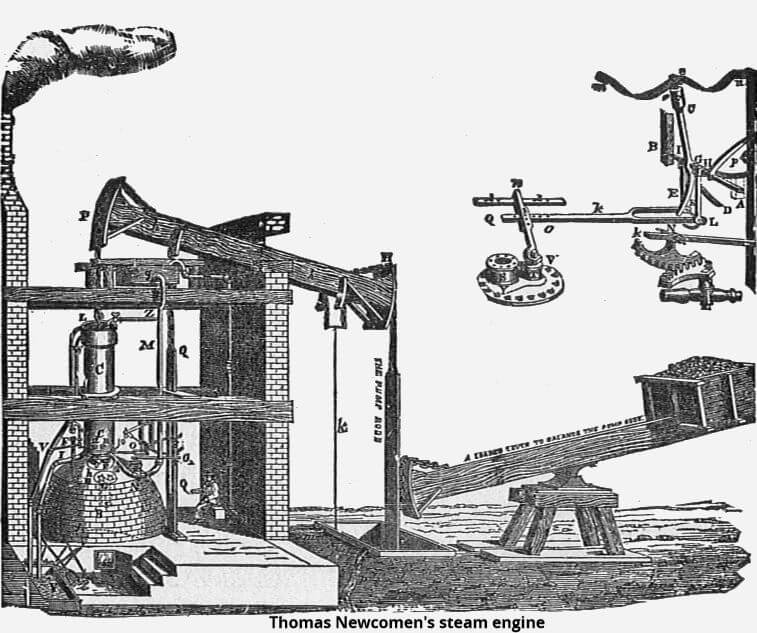
The first great tech leap forward was the steam engine, perfected in the 1760s by James Watt, but originally developed to pump water in coal mines by Thomas Newcomen in 1712. Steam was the workhorse of the Industrial Revolution, and the enabler of the management and expansion of the empire for Britain.
With steam, ships which had taken months to reach India got there in weeks and the great railways, whether in southern Africa or India, which were one of the hallmarks of the empire, were built.
Another invention which made communications throughout the empire possible was the electric telegraph, perfected by Samuel Morse in 1838.
But if there was one silver bullet, one invention that set Britain’s imperial ambitions ahead, it was the invention of the longitudinal chronometer, the first design of which was completed in 1730, but many modifications followed. The government had offered a substantial reward for a clock that could help its captains accurately establish their longitudinal positions. John Harrison’s chronometer gave British ships a great advantage: they knew where they were.
Other technical innovations included copper-sheathed hulls and eventually steam engines and iron hulls, leading to steel ships. Henry Bessemer made steel an available commodity with the Bessemer furnace in 1860, and soon British steel hulls upgraded naval fleets.
In 1733, the flying shuttle was invented which made Britain rich and enabled British fabric mills to process local wool and cotton from around the world, including America, India and Egypt.
Imperial Britain was a mercantile country (government working hand in hand with commerce) that insisted that all raw materials had to be transported to Britain to be processed, including cotton and jute, and even agricultural products like tea. To this day, tea is packaged in Britain and Ireland but grown in China, India, Sri Lanka, Africa and other countries.
Weaponry, importantly, also got the Brit-tech boost and played its role in the expansion of the empire. First came rifling of muskets to improve accuracy. Then came breech-loaded artillery and toward the end of the 19th century, the deadly Maxim Gun, a forerunner of the machine gun. Mass weapons manufacture assured British dominance.
Advances in medicine were important as well, especially in treating malaria and understanding tropical diseases. The use of quinine enabled troops in malarial areas, particularly in Africa, to recover. Keep the troops healthy and ready for combat.
My paternal grandfather was one of those. He was shipped from London to India and then to South Africa where he was demobilized at the end of the Boer War, which is how I came to grow up in the last vestiges of the empire and to understand some of the complexities of British rule.
For example, when it came to local administration, one size did not fit all. India was the Raj, the jewel in the crown. Southern Rhodesia, where I grew up, was the only self-governing colony in all but external affairs. Kenya Colony was just that; Malawi (Nyasaland) was a protectorate, as was Zambia (Northern Rhodesia) and Bechuanaland (Botswana). If in doubt about a rock or a country, the Brits claimed it fell under the monarch’s suzerainty. Good enough. It was red on the map.
Despite some imperial rumblings lately, America shouldn’t want and wouldn’t benefit from trying to assemble even a modest empire this late in the game. But America has had the tech benefits of empire since the British one faded, starting with India’s independence in 1947.
America filled the gap left by Britain as the dominant force in the world, admired, copied and envied. But underpinning that state of esteem and financial ease was tech leadership, medical leadership, and cultural leadership through film and television. America became the techno supremo.
Now government research funding is being butchered across the board from advanced energy to, most shameful of all, the philistine slashing of the National Institutes of Health’s research budgets.
Changing times doomed the British Empire, America’s future is at stake and it will be determined by technology and medicine. If we underfund research, the future is known.